February 22, 2024
CSEM and ClexBio create a bioreactor for tissue-engineered cardiovascular implants
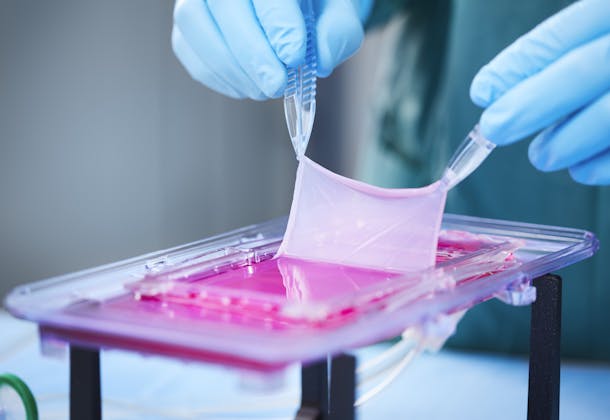
A new type of bioreactor that can grow human veins in the lab has been developed by CSEM and ClexBio, a Nordics-based startup specialized in regenerative medicine. Funded by the Research Council of Norway, their solution aims to improve the lives of millions of people suffering from severe chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) by providing them with bio-engineered vein implants.
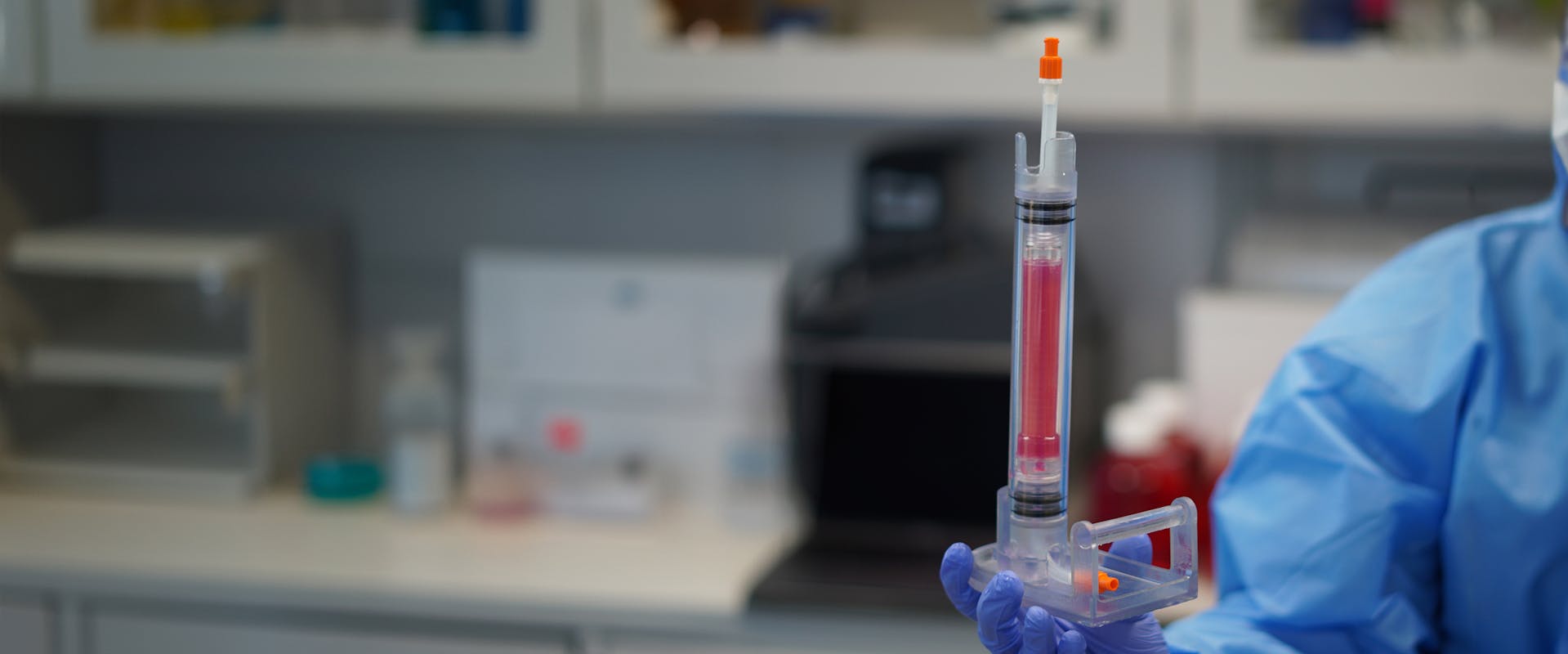
© CSEM - Engineering vein grafts comprised of human tissue material that integrates into the patient’s body and can turn into real, living tissue.


